Transient Flow around an Ahmed Body#
Features#
Solver:
lethe-fluid(with Q1-Q1)Transient problem
Displays how to import and easily adapt a gmsh file
Displays how to run case in parallel with mpirun
Files Used in This Example#
All files mentioned below are located in the example’s folder (examples/incompressible-flow/2d-ahmed-body).
Geometry file:
Ahmed-Body-20-2D.geoMesh file:
Ahmed-Body-20-2D.mshParameter file:
ahmed.prm
Description of the Case#
In this example we simulate the flow around a fixed Ahmed body (simplified version of a car, classical benchmark for aerodynamic simulation tools). The parameter file used is ahmed.prm.
The following schematic describes the simulated geometry.
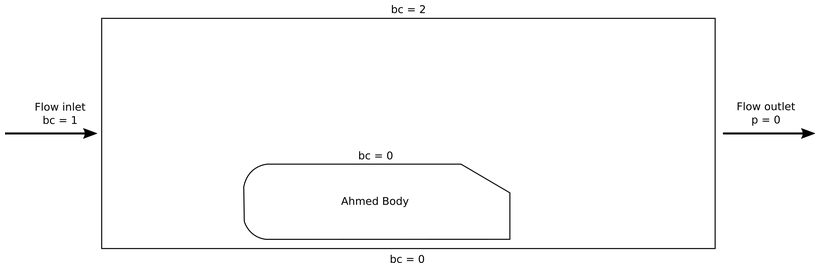
bc = 0 (No slip boundary condition)
bc = 1 (u = 1; flow in the x-direction)
bc = 2 (Slip boundary condition)
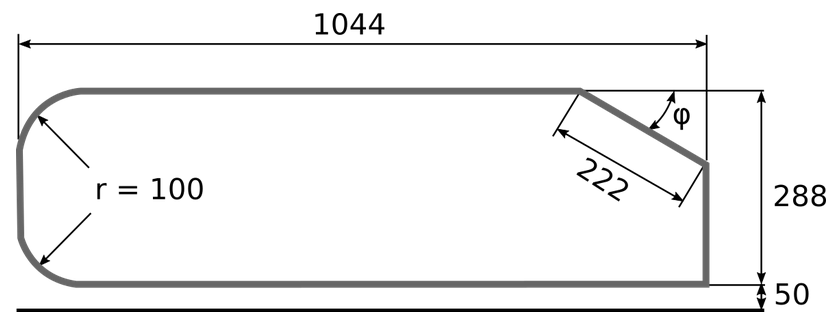
The basic geometry for the Ahmed body is given below, as defined in Ahmed et al. [1], with all measures in mm.
Parameter File#
First, we import the mesh as in the 2D Flow around a cylinder.
Mesh#
Geometry parameters can be adapted in the “Parameters” section of the .geo file, as shown below. For instance, the step parameter phi could be changed.
//===========================================================================
//Parameters
//===========================================================================
unit = 1000; //length unit : 1 -> mm ; 1000 -> m
phi = 20; //angle at rear, variable
esf = 2.0e-1; //element size factor, used in the free quad mesh
//Ahmed body basic geometry
L = 1044/unit;
H = 288/unit;
R = 100/unit;
Hw = 50/unit; //wheel height (height from the road)
Ls = 222/unit; //slope length
//Fluid domain
xmin = -500/unit;
ymin = -Hw;
xmax = 2500/unit;
ymax = 1000/unit;
The initial Mesh is built with Gmsh. It is defined as transfinite at the body boundary layer and between the body and the road, and free for the rest of the domain. The mesh is dynamically refined throughout the simulation. This will be explained later in this example.
The input mesh Ahmed-Body-20-2D.msh is in the same folder as the .prm file. The mesh subsection is set to use this file.
subsection mesh
set type = gmsh
set file name = Ahmed-Body-20-2D.msh
end
Important
For further information about Meshing, we refer to the reader to the Introduction on How to Use GMSH page of this documentation, or the GridGenerator on the deal.ii documentation and the Gmsh website.
Initial and Boundary Conditions#
The Initial Conditions and the Boundary Conditions are defined as in Example 3.
subsection initial conditions
set type = nodal
subsection uvwp
set Function expression = 1; 0; 0
end
end
subsection boundary conditions
set number = 3
subsection bc 0
set type = noslip
end
subsection bc 1
set type = function
subsection u
set Function expression = 1
end
subsection v
set Function expression = 0
end
subsection w
set Function expression = 0
end
end
subsection bc 2
set type = slip
end
end
Simulation Control#
Time integration is defined by a 1st order backward differentiation (bdf1), for a 4 seconds simulation (time end) with a 0.01 second time step. The output path is defined to save obtained results in a sub-directory, as stated in Simulation Control:
subsection simulation control
set method = bdf1
set output frequency = 1
set output name = ahmed-output
set output path = ./Re720/
set time end = 4
set time step = 0.01
end
Ahmed bodies are typically studied considering a 60 m/s flow of air. Here, the flow speed is set to 1 (u = 1) so that the Reynolds number for the simulation (Re = uL/ν, with L the height of the Ahmed body) is varied by changing the kinematic viscosity:
subsection physical properties
subsection fluid 0
set kinematic viscosity = 4e-4
end
end
Running the Simulation#
We launch the simulation from the same folder as the .prm and .msh file, using the lethe-fluid solver. To decrease simulation time, it is advised to run on multiple CPU cores, using mpirun:
To do so, copy and paste the lethe-fluid executable to the same folder as your .prm file and launch it running the following line:
where 6 is the number of CPUs used. The estimated execution time for a 4 seconds simulation with 6 CPUs is 6 minutes and 53 seconds. For 1 CPU, the estimated time is 30 minutes and 37 seconds.
Alternatively, specify the path to the lethe-fluid in your build/applications folder, as follows:
Guidelines for parameters other than the previous mentioned are found at the Parameters guide.
Results#
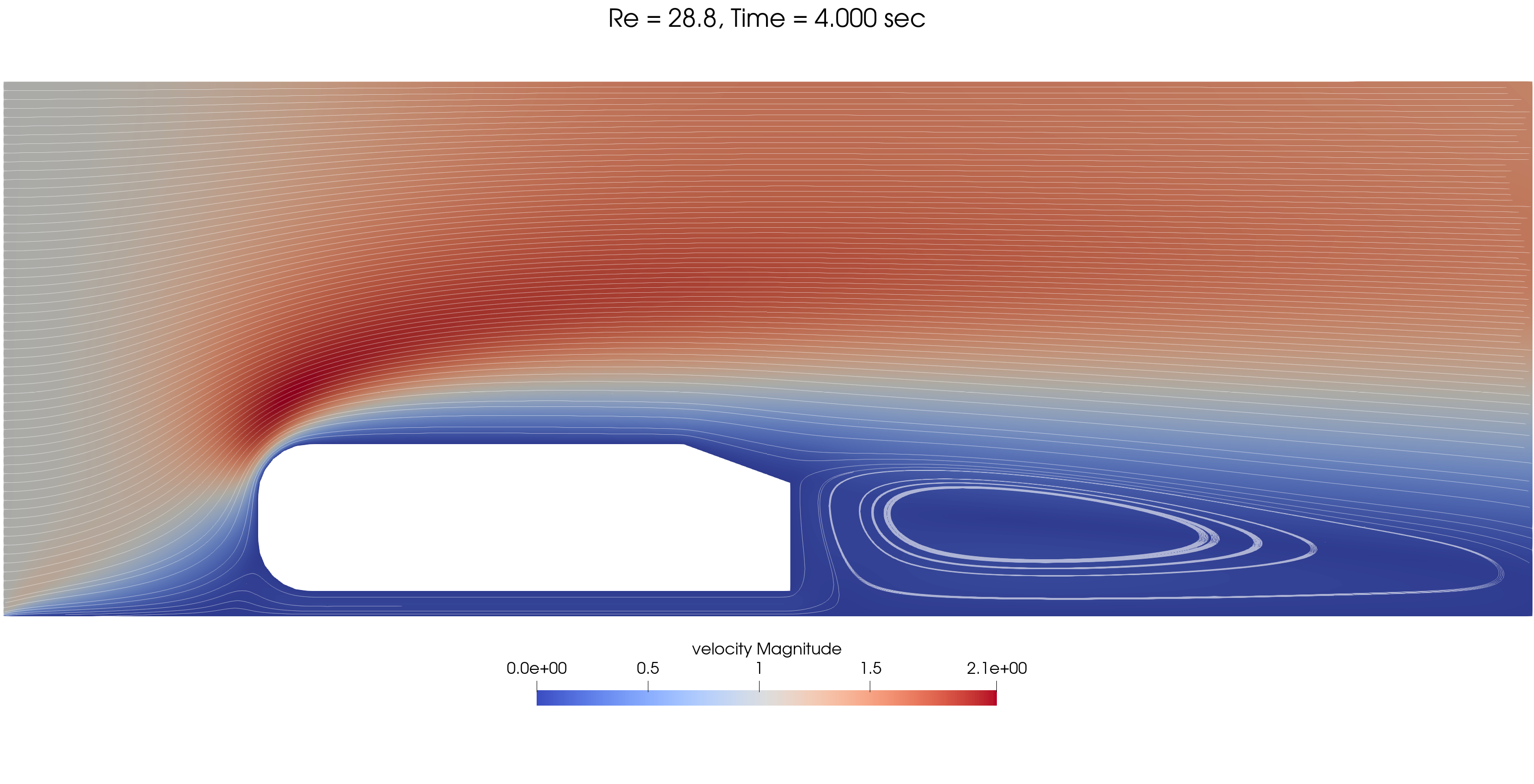
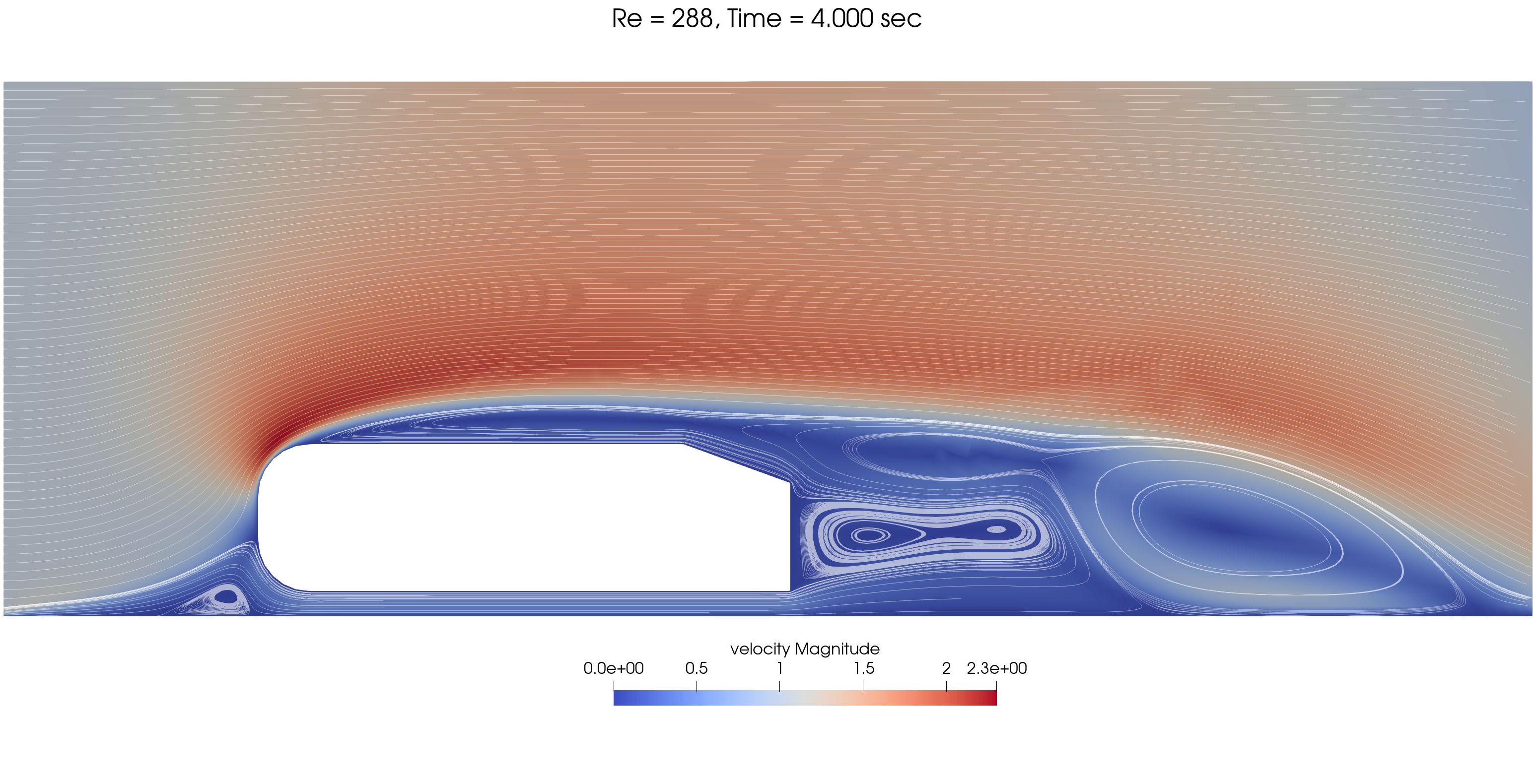
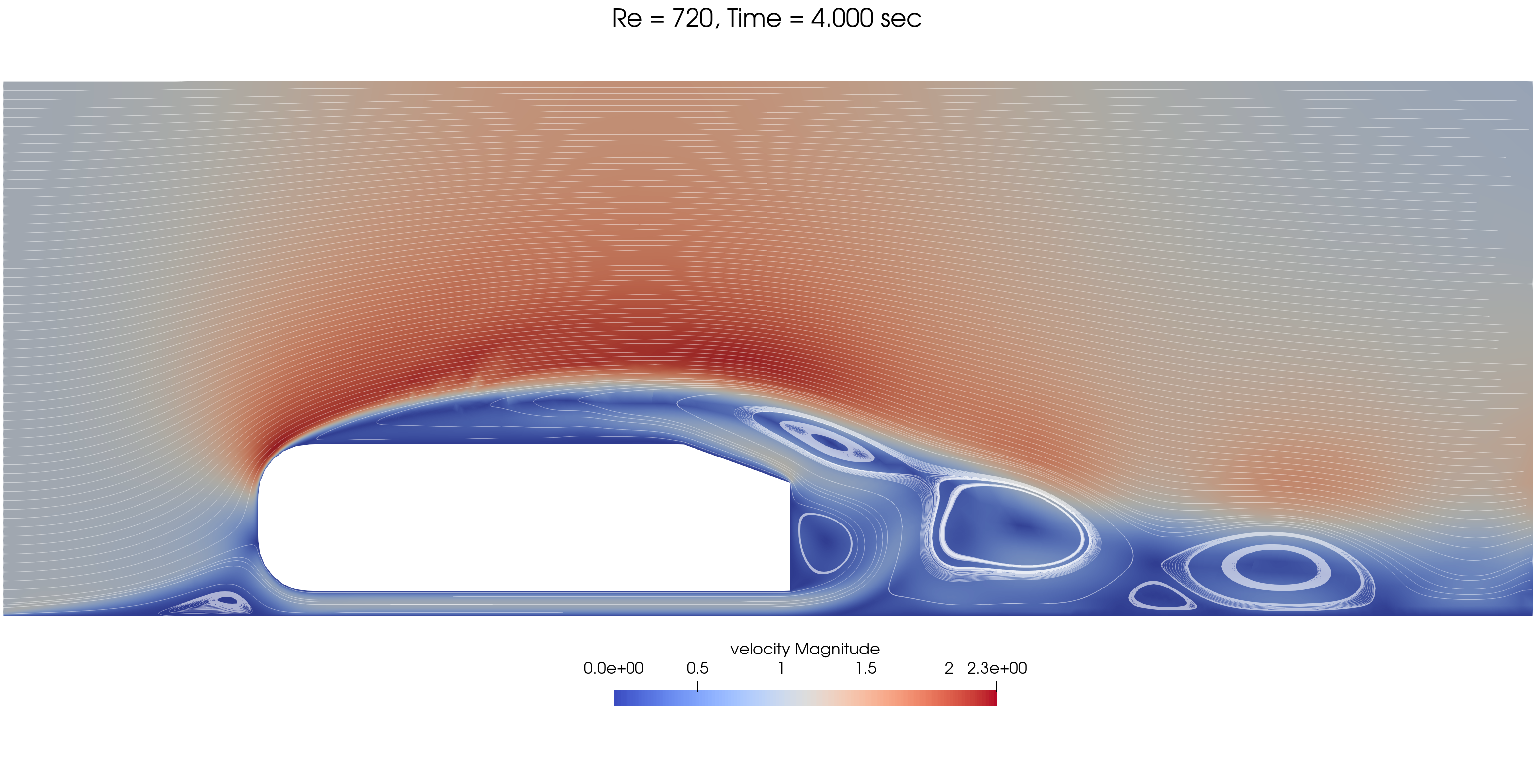
Transient results are shown for three Re values:
The mesh and processors load is adapted dynamically throughout the simulation, as shown below for Re = 720.
Time |
Image |
|---|---|
t = 0 s |
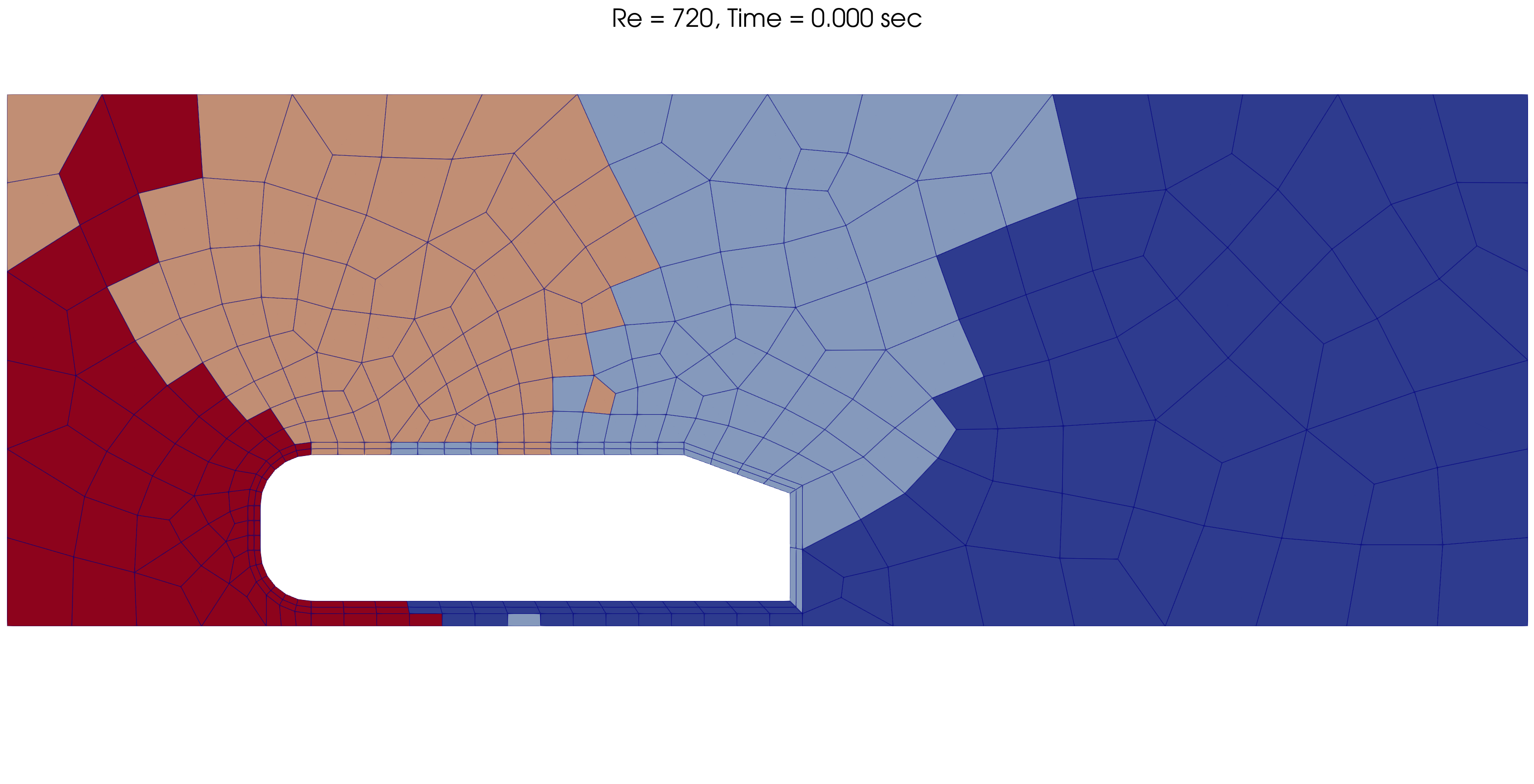
|
t = 0.05 s |
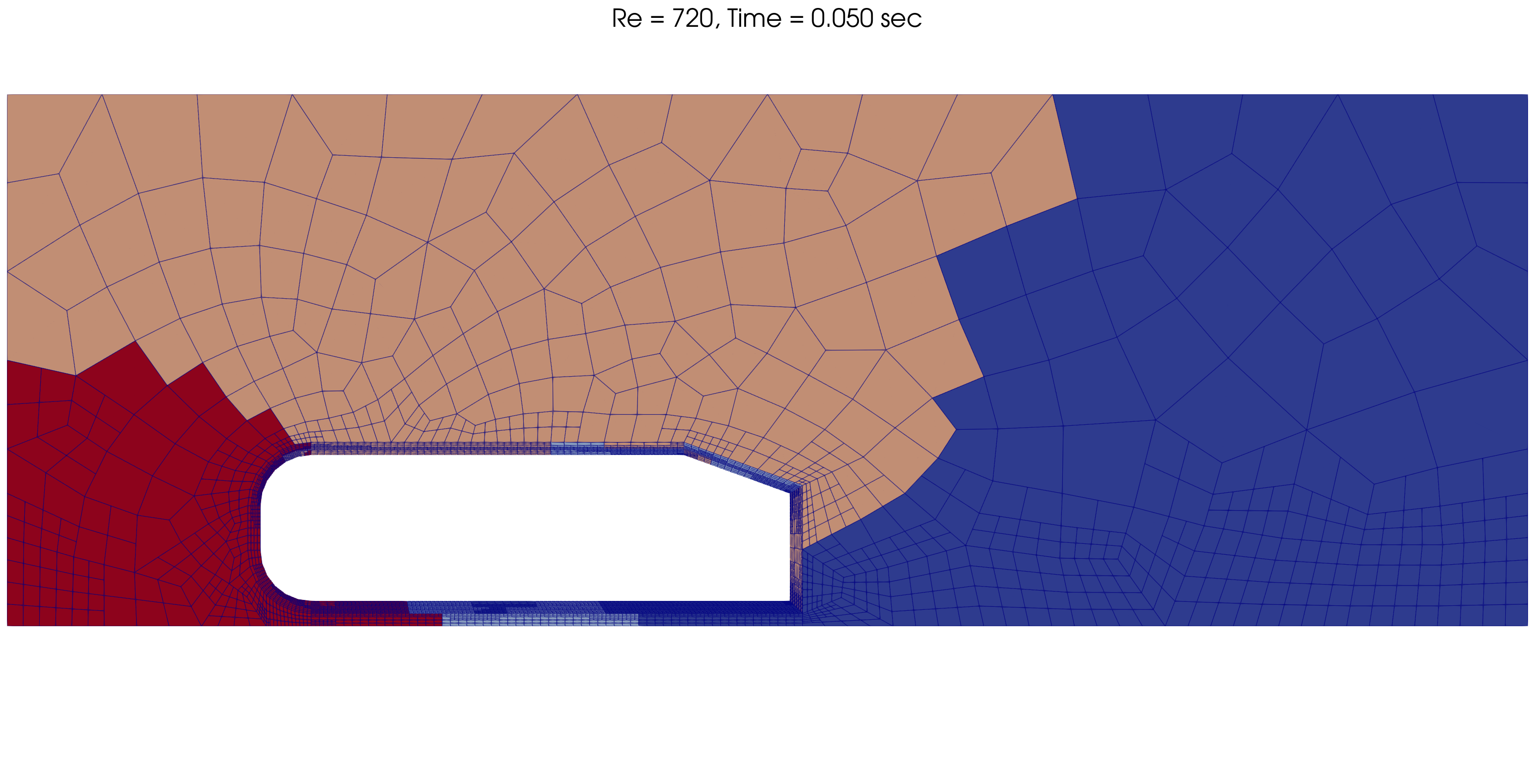
|
t = 4 s |
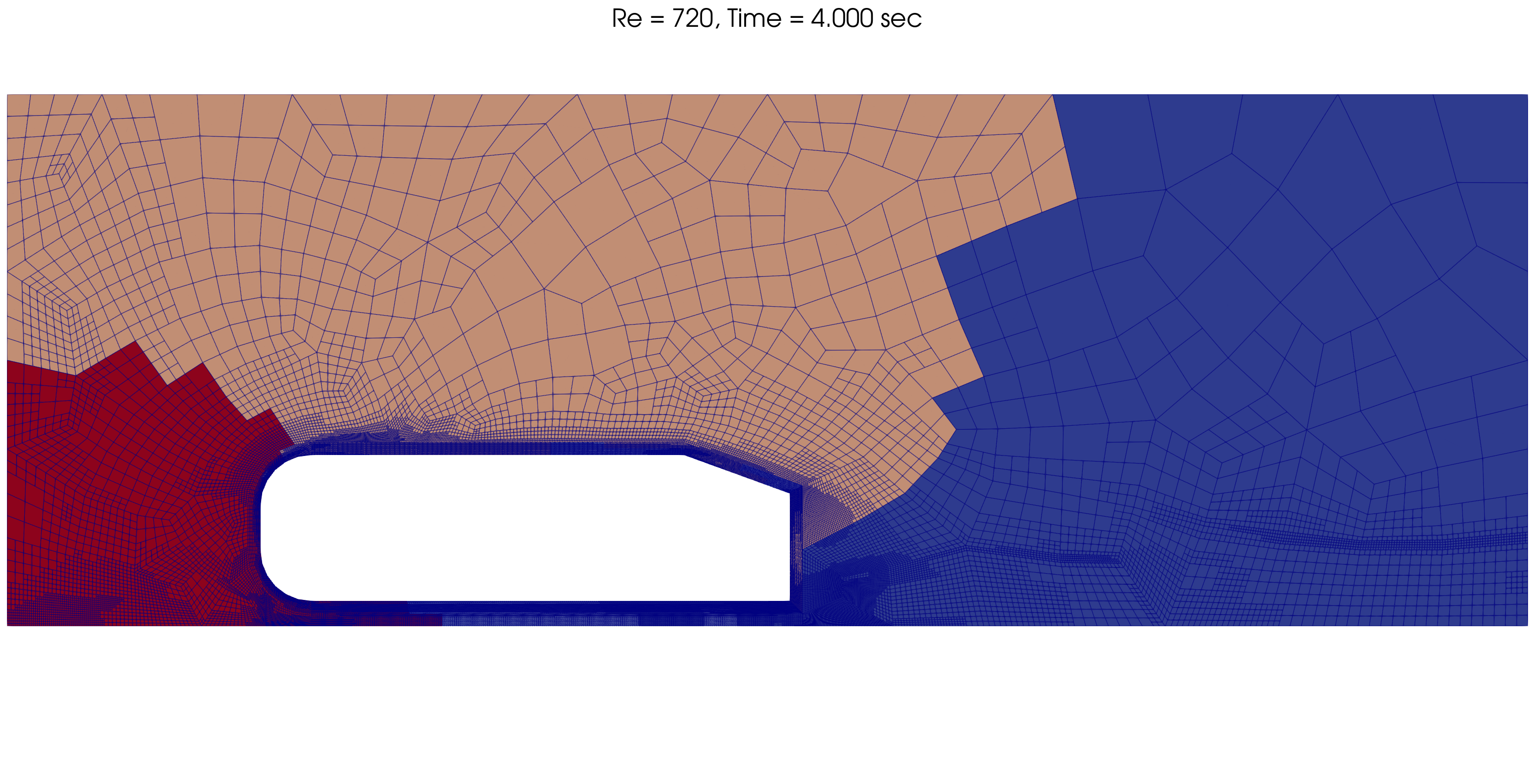
|
Possibilities for Extension#
Change the
phivalue to see the effect of the angle in the streamline.Vary the Reynolds number, or the initial and boundary conditions.
Make a three-dimensional mesh, or even add other features to it, such as sharpen the edges.
Test higher order elements (e.g., Q2-Q1).